Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an MCP server and why do platform engineers need them?
An MCP (Model Context Protocol) server is a standardized interface that enables AI coding assistants to interact with external tools and services through natural language commands. Platform engineers need them because they eliminate the constant context switching between IDEs, terminals, cloud consoles, monitoring dashboards, and incident management systems. Instead of running manual commands or clicking through web interfaces, platform engineers can ask their AI assistant to "deploy this infrastructure" or "show me failing pods" and get immediate results—all without leaving their development environment.
2. Which MCP servers are production-ready versus experimental?
Production Ready (Enterprise-backed): StackGen MCP, Terraform MCP, GitHub MCP, Azure DevOps MCP, AWS Billing MCP, Datadog MCP, and PagerDuty MCP are all actively maintained by enterprise vendors with stable APIs and recommended for production use.
Beta (Community-driven): Kubernetes MCP, Prometheus MCP, and ArgoCD MCP are community-driven with active development, suitable for non-critical workloads but may have occasional breaking changes.
The enterprise-backed MCPs from Microsoft, AWS, HashiCorp, Datadog, and PagerDuty receive professional support and sustained development, making them safer choices for production infrastructure workflows.
3. How do I choose the right MCP server for infrastructure provisioning?
The choice depends on your team's workflow and governance requirements:
Choose StackGen MCP if your platform team needs to enable developer self-service while maintaining governance and compliance controls. StackGen's blueprint approach lets platform engineers encode security policies once, then safely scale infrastructure access across development teams. This is ideal for organizations with 50+ developers where manual infrastructure reviews have become a bottleneck.
Choose Terraform MCP if your team is deeply invested in Terraform and primarily needs faster access to Terraform operations (state queries, plan/apply) from your IDE. Terraform MCP works with your existing Terraform codebase but focuses on accelerating experienced platform engineers' direct infrastructure work rather than enabling broader self-service patterns.
Many teams use both: StackGen MCP for governed developer self-service and Terraform MCP for platform engineers' direct infrastructure operations.
4. How do observability MCPs (Prometheus, Datadog) compare for incident response?
Prometheus MCP excels for teams already using Prometheus and Grafana for monitoring. It translates natural language into PromQL queries, making metrics accessible even to team members who don't know the query language. Best for open-source monitoring stacks and teams wanting to avoid vendor lock-in.
Datadog MCP provides unified access to logs, metrics, traces, and APM data through a single interface. It's more comprehensive than Prometheus MCP alone because it correlates multiple observability signals automatically. Best for teams already paying for Datadog who want to eliminate context switching between Datadog's various product areas during incident response.
Both eliminate the need to open monitoring dashboards during troubleshooting, but Datadog MCP offers richer correlation capabilities while Prometheus MCP provides more control and avoids vendor dependency.
5. Can I use multiple MCP servers together?
Yes—in fact, most platform engineering teams should use multiple MCP servers together. The MCPs complement each other for different workflow stages. For example:
- Infrastructure deployment: StackGen MCP or Terraform MCP provisions resources.
- CI/CD: GitHub MCP or Azure DevOps MCP monitors deployments.
- Observability: Kubernetes MCP + Prometheus MCP or Datadog MCP diagnose issues.
- Incident coordination: PagerDuty MCP manages alert escalation.
- Cost optimization: AWS Billing MCP tracks spending impact.
A typical incident response workflow might use: Kubernetes MCP to check pod status → Prometheus MCP or Datadog MCP to analyze metrics → GitHub MCP to review recent deployments → PagerDuty MCP to coordinate team response. All from a single IDE conversation without switching tools.
6. Are enterprise-backed MCPs (Microsoft, AWS, HashiCorp) better than community options? Enterprise-backed MCPs from Microsoft, AWS, HashiCorp, StackGen, Datadog, and PagerDuty generally offer:
- Guaranteed long-term support and development
- Professional documentation and troubleshooting resources
- Stable APIs with proper versioning and deprecation notices
- Integration with enterprise support contracts
- Security audits and compliance certifications
Community-driven MCPs (Kubernetes, Prometheus, ArgoCD) offer:
- Faster iteration and new features
- Greater transparency and community input
- No vendor lock-in
- Free and open-source
For production infrastructure workflows, start with enterprise-backed MCPs like
StackGen, Terraform, GitHub, Azure DevOps, AWS Billing, Datadog, and PagerDuty. Add community MCPs like
Kubernetes, Prometheus, and ArgoCD for non-critical workflows or after your team has experience with MCP adoption.
Want more detailed guidance? See our complete MCP FAQ guide covering setup, security, troubleshooting, and advanced use cases.

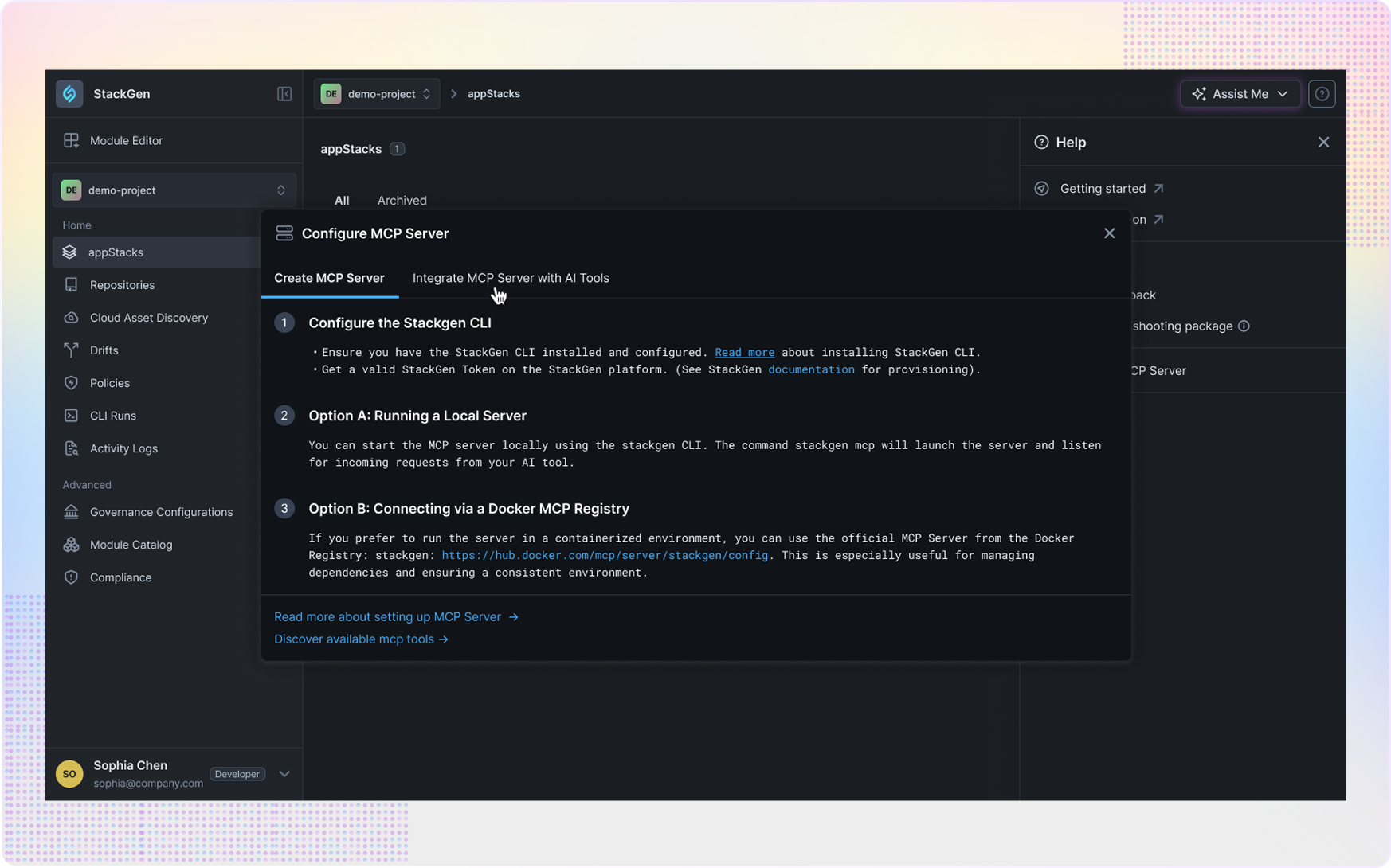 StackGen MCP is a comprehensive infrastructure lifecycle management platform built specifically for platform engineering teams who need to balance developer velocity with enterprise governance. Instead of manually reviewing every infrastructure request and running approval workflows, platform engineers can create pre-approved blueprints that encode security and compliance requirements, then enable developers to self-serve infrastructure provisioning safely.
StackGen MCP is a comprehensive infrastructure lifecycle management platform built specifically for platform engineering teams who need to balance developer velocity with enterprise governance. Instead of manually reviewing every infrastructure request and running approval workflows, platform engineers can create pre-approved blueprints that encode security and compliance requirements, then enable developers to self-serve infrastructure provisioning safely. 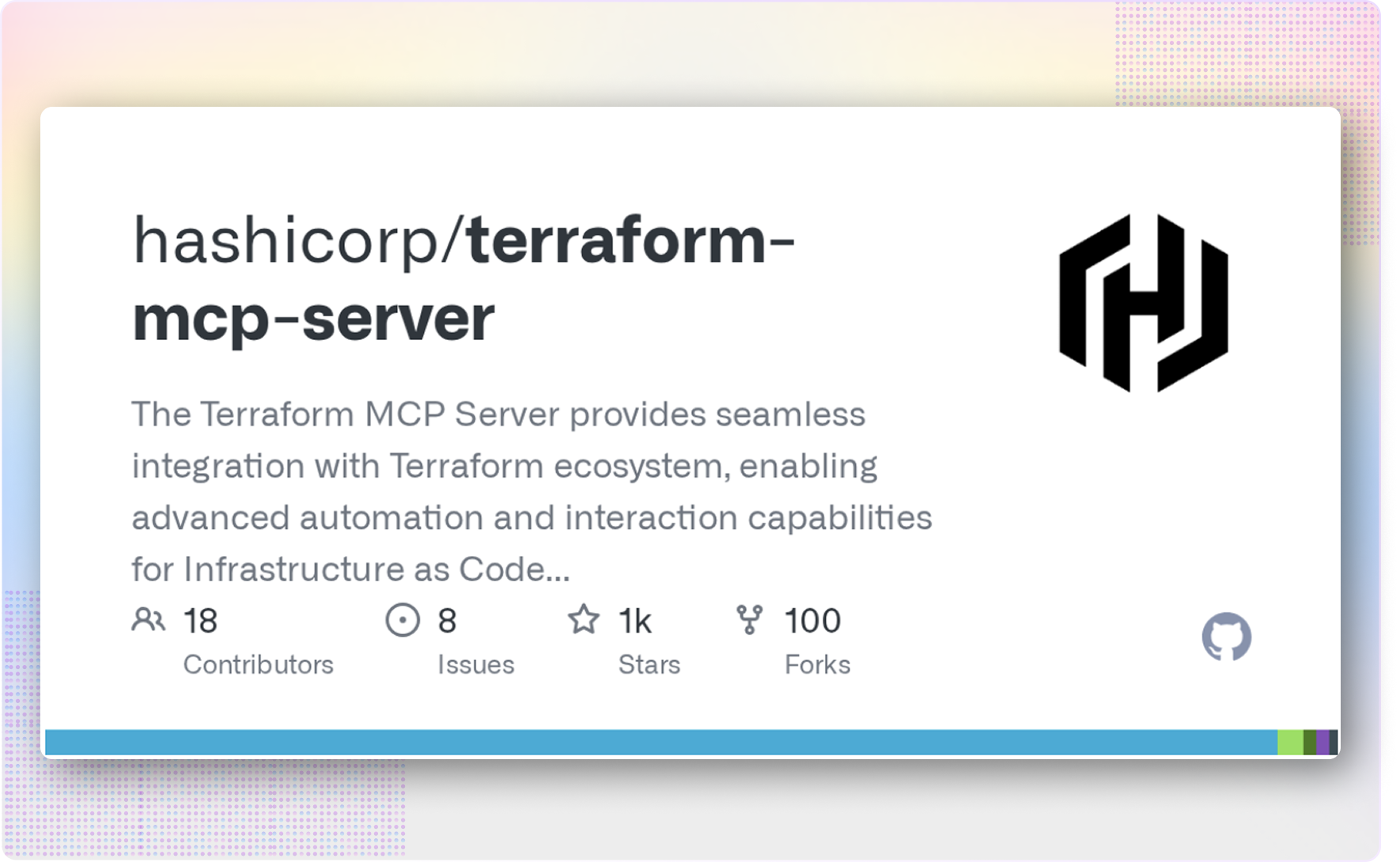 The
The 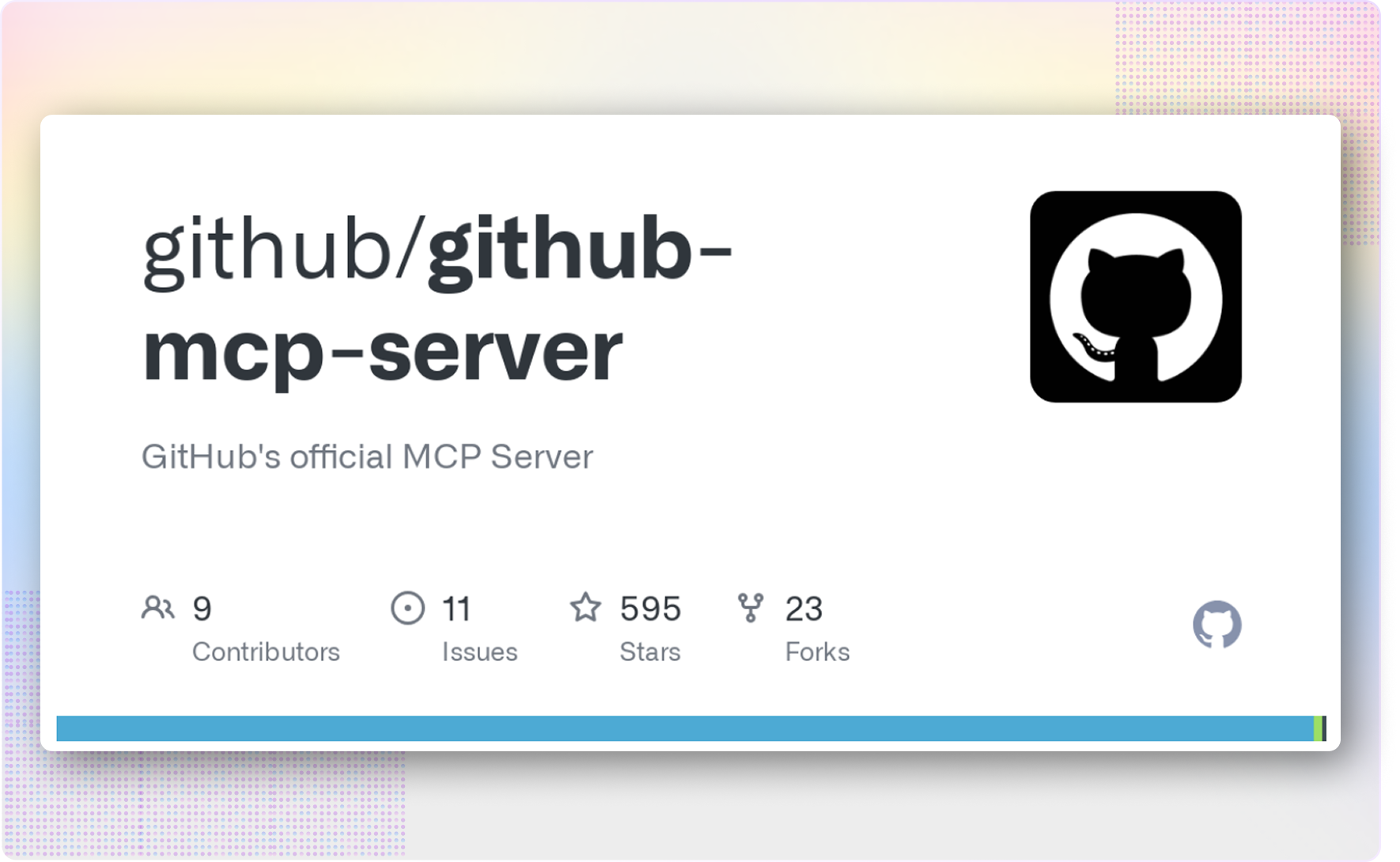 The
The  The
The  The
The  The
The  The
The  The
The  The
The  The
The